Countering Violent Extremism & Terrorism
Countering Violent Extremism & Terrorism
Violent extremists (VE) are individuals who support and/or commit ideologically-motivated violence to further political agendas. Countering violent extremism (CVE) therefore encompasses the preventative aspects of counter-terrorism (CT) to undermine the attraction of extremist organizations, and ideology that promotes violence. Methods include specific community-led awareness, interventions and counter narratives.
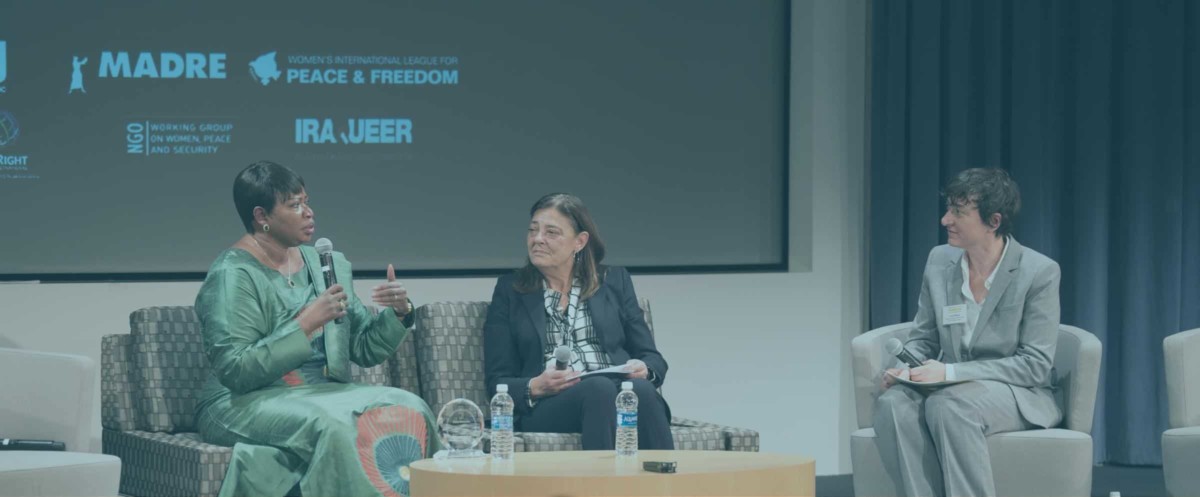
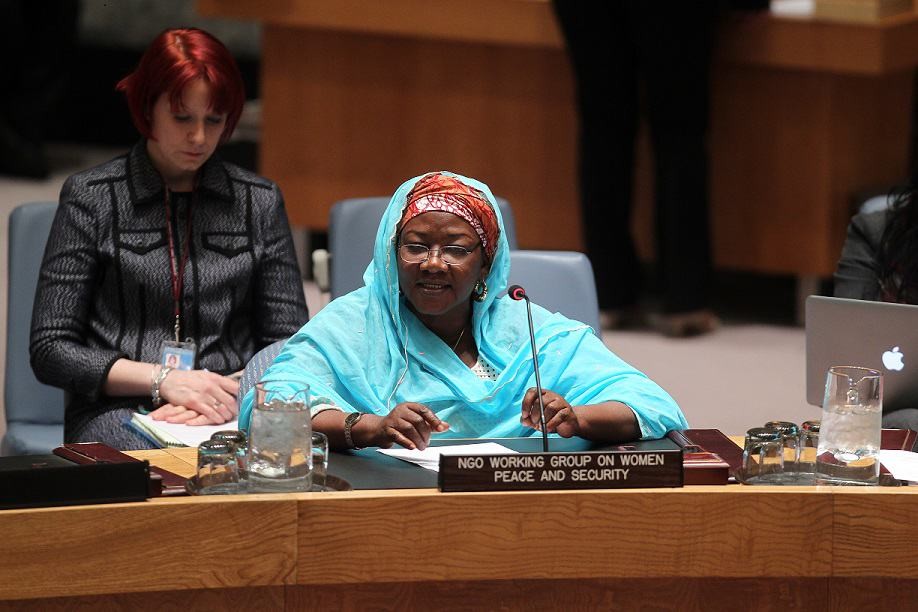
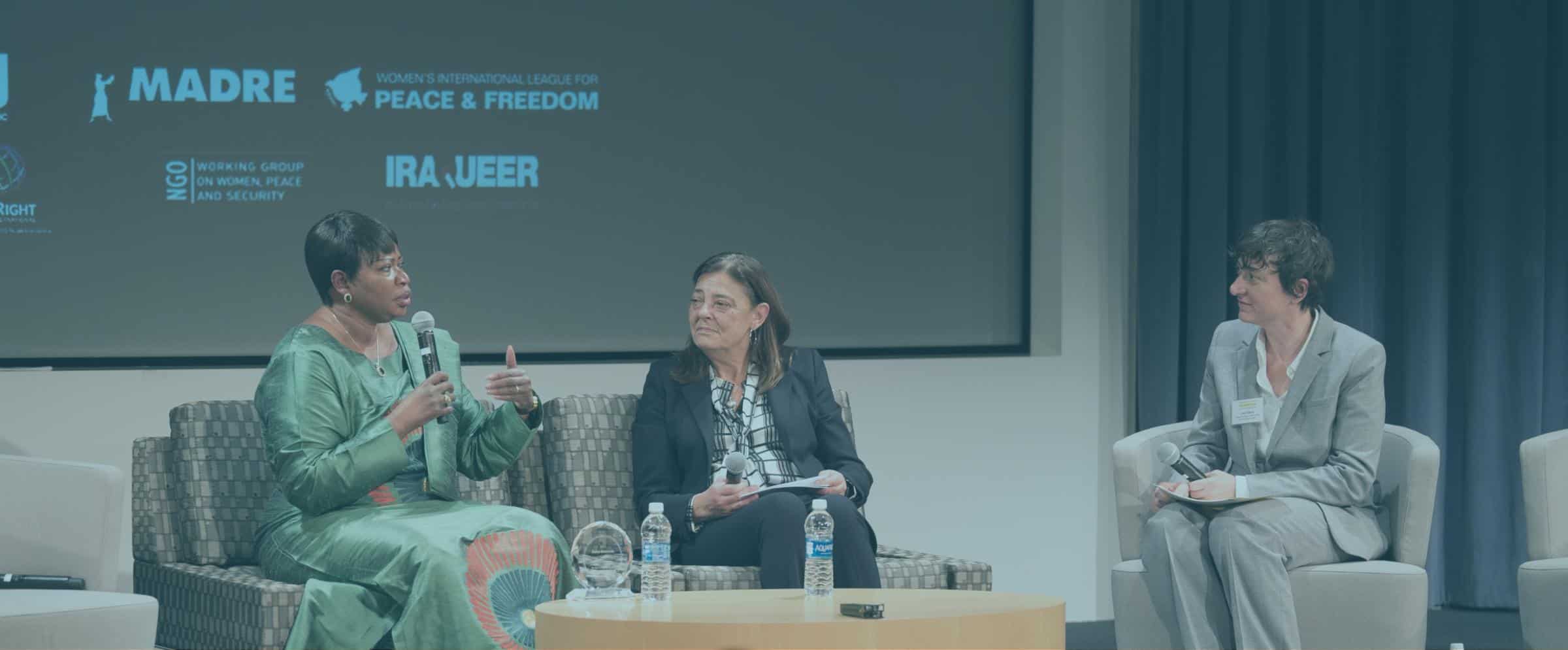
In the context of the recent global spread of violent extremism, which systematically targets women and employs sexual and gender-based violence, the NGO Working Group works to ensure the UN Security Council and Member States incorporate WPS (Women, Peace and Security) resolutions and best practices. These 7 Provisions are the result of fifteen years of work on WPS, in all actions to countering violent extremism and counter-terrorism policies. In particular, the NGO Working Group advocates for the inclusion of gender analysis and monitoring, to better understand the dynamics and impacts of violent extremism on women, including recognizing the broad range of roles women play in supporting and countering violent extremism.
In addition, the NGOWG advocates for changes to the mandate of the UN Committee on Counter-terrorism, guided by resolutions 1373 (2001) and 1624 (2005), to ensure that women and women civil society organizations are consulted, and are granted full and equal participation in formal processes of CVE and CT at the international, regional and national level.
Current and Past Recommendations to the UN Security Council (Monthly Action Points)
The Council is due to renew the mandate of its Counter-Terrorism Committee Executive Directorate (CTED). As recalled in SCR 1805 (2008), CTED is mandated to advise on the compliance of counter-terrorism measures with international human rights, refugee and humanitarian law. In renewing CTED’s mandate, the Council should ensure that UN advice and technical assistance, including through country visits, considers the specific impact of terrorism and counter-terrorism measures on women and girls. This requires continued and strengthened cooperation with relevant UN entities, including UN Women and the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights.
Relevant Resources