Iraq
Iraq
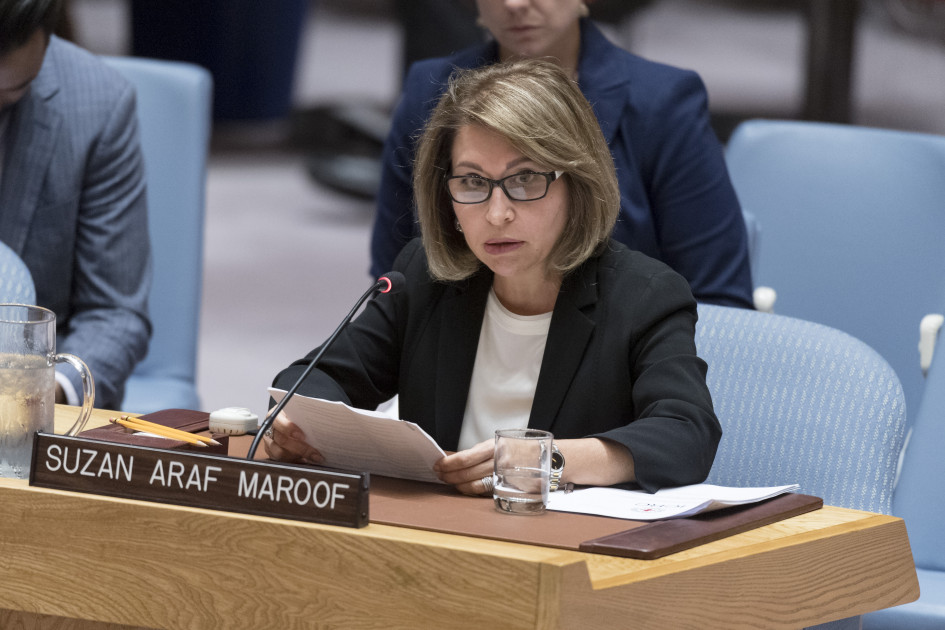
Women are crucial allies to the efforts to eliminate extremism in Iraq. The Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) has contributed to a political landscape in Iraq historically characterized by sectarianism, ineffective judicial systems, high levels of government corruption, and high rates of violence against women, including sexual and gender-based violence. ISIL continues to use sexual and gender-based violence and rape as weapons of war— and targets women, particularly Yazidi women and other non-Shiite minorities, for sexual slavery among fighters.
Iraq acceded to the Convention on the Elimination of all Forms of Discrimination against Women (CEDAW) in 1986, launched the National Strategy on Combating Violence against Women in 2013, and launched its National Action Plan pursuant to Resolution 1325 in 2014. Iraq’s National Action Plan was the first launched in the Middle East. The Ministry of Women’s Affairs in Iraq has also developed a National Strategy for the Advancement of Iraqi Women, but due to the political climate it hasn’t been effectively implemented; similarly, laws banning forced and early marriages are rarely enforced.
Based on the work of NGOWG members and their partners, the NGOWG advocates for the Government of Iraq to clarify their shelter policies, in order to allow and support Iraqi NGOs in their efforts to operate shelters and provide much needed services to survivors of SGBV. Further, the NGOWG urges the Security Council to ensure that the United Nations Assistance Mission for Iraq (UNAMI) is regularly engaging with women’s organizations, and will continue to take concrete steps to support women’s participation in all peace and security processes.
Current and Past Recommendations to the UN Security Council (Monthly Action Points)
The forthcoming report from the UN Assistance Mission in Iraq (UNAMI) should reflect the current humanitarian situation, including the situation for the approximately 1.3 million internally displaced people (IDPs), many of whom are members of female-headed households, and should also detail how the mission will concretely address this situation. Due to access constraints, the current humanitarian response is inadequate, with most of the IDPs living in squatter communities, and women in particular facing extreme vulnerability. The Council should ensure that despite the transition from humanitarian assistance to recovery, the concerns of vulnerable Iraqis, especially women, are met by UNAMI and other UN agencies on the ground.
Relevant Resources